Here we provide greater detail on the content of the Domestic EPC. If you require detail of the Commercial EPC please click here.
The domestic energy performance certificate
The SAP Crown logo at the top of the EPC shows the EPC uses the The Standard Assessment Procedure (SAP) which is the methodology used by the Government to assess and compare the energy and environmental performance of dwellings.]
The main property details then include:
- The address;
- The type of dwelling (flat, house etc);
- The date of the Energy Assessment survey
- The date when the Certificate was lodged on the Central Regiser;
- The unique Report Reference Number assigned to the EPC when it is lodged;
- And the floor area of the property that was used as part of the assessment calculation. This could exclude some conservatories that are thermally seperated from the house ie that they have externally quality doors between them and the house. It will also exclude any unheated garages.
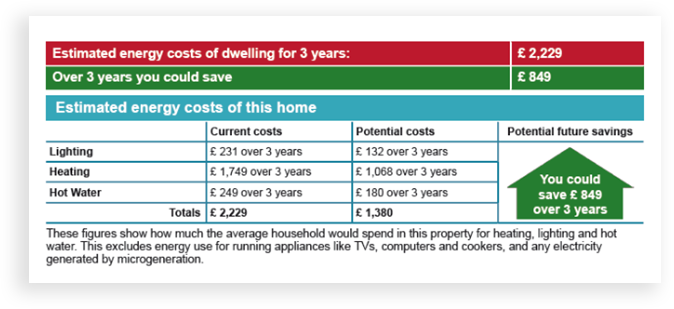
EPC estimated energy costs
The domestic EPC will show the estimated energy costs for the property based on standard occupancy. It will also show the potential savings if certain energy efficiency improvments are undertaken.
- Lighting. The property ideally needs all fixed lighting to be either LED or fluorescent fittings.
- Heating. This figures relates to the central heating, usually radiators, or storage heaters.
- Hot water. This is for showers, baths and basins.
The figures indicate how much the average household would spend on hot water, lighting and heating. This figures exclude all appliances and computers.
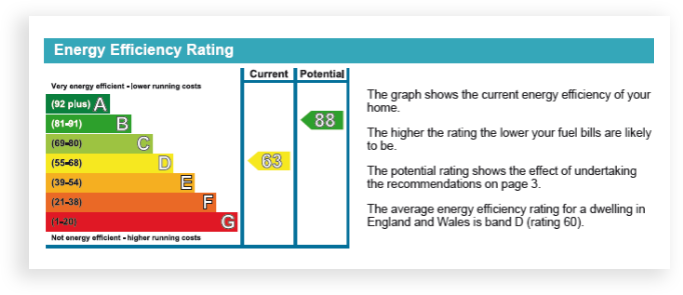
the energy efficiency rating
Properties are graded A to G with the everage property in Band D. Generally old properties with electric or poor amounts of insulation will be in the lower bands. For a property to achieve a Band A it will need to be extremely well insulated with a modern heating system and solar panels.
Potential rating shows what could be achieved if all the recommended improvments to the energy efficiency were installed at the property.
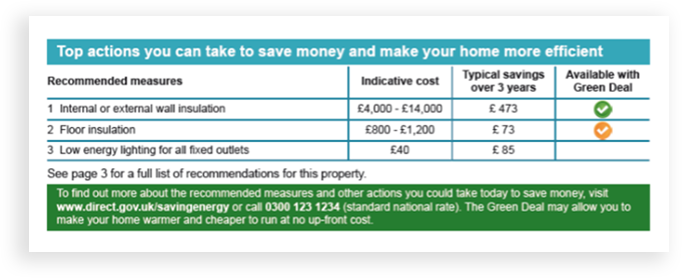
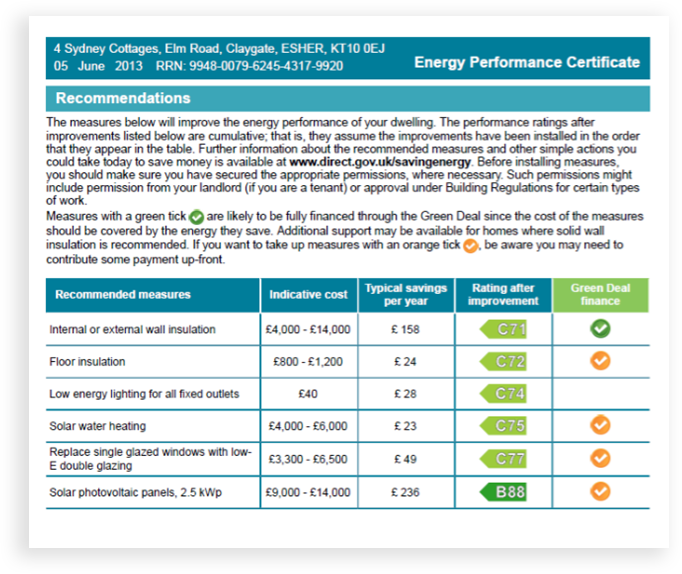
top EPC recommendations
These efficiency improvements are listed that offer the best payback on investment. Wall insulation on this particular Victorian property offers the highest savings although the indicative costs to install are high. Potential payback period in 8.5 years in this instance.
The green tick shown under the Green Deal shows that finance could be available to help with installation costs.
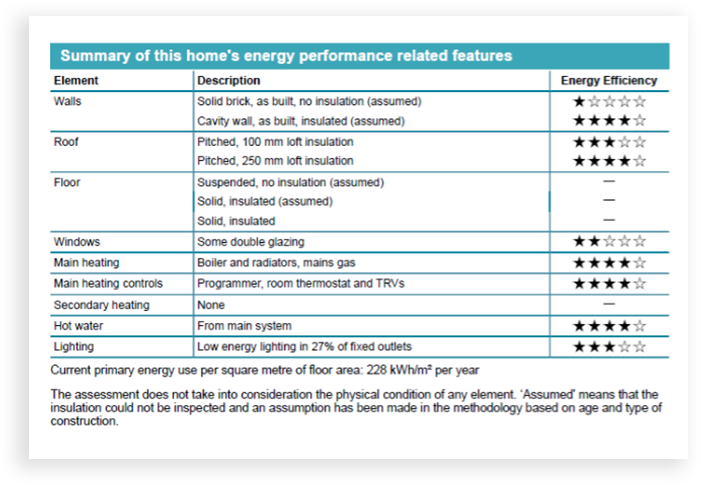
energy performance certificate summary of energy features
Each building element and heating component on the property is listed with a short description and a simple star rating. Old solid brick properties will have 1 star and newly build walls will have 4 or 5 stars.
With respect to heating, electric heaters have 1 star and mains gas heaters 4 stars.
A figure is provided for the primamry energy use per square meter of the floor area in kWh/meter square.
The assessment does not take into consideration the physical condition of the elenents.
Assumed means the insualtion could not be inspected and an assumption has been made in the methodology based on the age and type of construction.
Further Information On Recommendations
Loft Insulation
Loft insulation laid in the loft space or between roof rafters to a depth of at least 270 mm will significantly reduce heat loss through the roof; this will improve levels of comfort, reduce energy use and lower fuel bills. Insulation should not be placed below any cold water storage tank, any such tank should also be insulated on its sides and top, and there should be boarding on battens over the insulation to provide safe access between the loft hatch and the cold water tank. The insulation can be installed by professional contractors but also by a capable DIY enthusiast. Loose granules may be used instead of insulation quilt; this form of loft insulation can be blown into place and can be useful where access is difficult. The loft space must have adequate ventilation to prevent dampness; seek advice about this if unsure. Further information about loft insulation and details of local contractors can be obtained from the National
Insulation Association.
Cavity wall insulation
Cavity wall insulation, to fill the gap between the inner and outer layers of external walls with an insulating material, reduces heat loss; this will improve levels of comfort, reduce energy use and lower fuel bills. The insulation material is pumped into the gap through small holes that are drilled into the outer walls, and the holes are made good afterwards. As specialist machinery is used to fill the cavity, a professional installation company should carry out this work, and they should carry out a thorough survey before commencing work to ensure that this type of insulation is suitable for this home. They should also provide a guarantee for the work and handle any building control issues. Further information about cavity wall insulation and details of local installers can be obtained from the National Insulation Association. (link above).
New condensing boiler
A condensing boiler is capable of much higher efficiencies than other types of boiler, meaning it will burn less fuel to heat this property. This improvement is most appropriate when the existing central heating boiler needs repair or replacement, but there may be exceptional circumstances making this impractical. Condensing boilers need a drain for the condensate which limits their location; remember this when considering remodelling the room containing the existing boiler even if the latter is to be retained for the time being (for example a kitchen makeover). Building Regulations apply to this work, so your local authority building control department should be informed, unless the installer is registered with a competent persons scheme¹, and can therefore selfcertify the work for Building Regulation compliance. Ask a qualified heating engineer to explain the options.
Internal or external wall insulation
Solid wall insulation involves adding a layer of insulation to either the inside or the outside surface of the external walls, which reduces heat loss and lowers fuel bills. As it is more expensive than cavity wall insulation it is only recommended for walls without a cavity, or where for technical reasons a cavity cannot be filled. Internal insulation, known as drylining, is where a layer of insulation is fixed to the inside surface of external walls; this type of insulation is best applied when rooms require redecorating and can be installed by a competent DIY enthusiast. External solid wall insulation is the application of an insulant and a weatherprotective finish to the outside of the wall. This may improve the look of the home, particularly where existing brickwork or rendering is poor, and will provide longlasting weather protection. Further information can be obtained from the National Insulation Association. It should be noted that planning permission might be required.
Solar photovoltaic (PV) panels
A solar PV system is one which converts light directly into electricity via panels placed on the roof with no waste and no emissions. This electricity is used throughout the home in the same way as the electricity purchased from an energy supplier. The British Photovoltaic Association has up-to-date information on local installers who are qualified electricians and on any grant that may be available. Planning restrictions may apply in certain neighbourhoods and you should check this with the local authority. Building Regulations apply to this work, so your local authority building control department should be informed, unless the installer is appropriately qualified and registered as such with a competent persons scheme¹, and can therefore self-certify the work for Building Regulation compliance. The assessment does not include the effect of any feed-in tariff, which could appreciably increase the savings that are shown on this EPC for solar photovoltaic panels.